
PTFE Plastic (Polytetrafluoroethylene, Teflon) Selection Guide
Polytetrafluoroethylene, commonly known as PTFE or Teflon®, is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and non-stick properties. In this web page, we will explore the different types of PTFE, its numerous advantages and disadvantages, and the diverse industrial applications where PTFE plays a crucial role.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene, Teflon®) rapid manufacturing, & custom molded parts are available now!
Check with one of Canyon’s helpful product engineers for an expert material and manufacturing recommendation.
Common names include: PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene, Teflon®), Trade Names: Teflon®, Fluon®, Dyneon™ PTFE, Gore-Tex® PTFE, Halopolymer PTFE, Polyflon®.

Advantages
- Exceptional Chemical Resistance: PTFE is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, acids, bases, and solvents, making it suitable for use in corrosive environments.
- Low Friction: PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, providing excellent non-stick and low-wear properties. It is often used in applications requiring lubricity.
- Wide Temperature Range: PTFE can withstand a broad temperature range, from cryogenic temperatures to high heat without losing its properties.
- Electrical Insulation: PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator and is often used in electrical and electronic applications.
- Biocompatibility: PTFE is biologically inert and is suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications.
- Non-toxic: PTFE is non-toxic, making it safe for food-contact applications.
- Low Surface Energy: PTFE's low surface energy makes it highly repellent to water and oils, contributing to its non-stick properties.
Disadvantages
- Limited Mechanical Strength: PTFE has relatively low mechanical strength compared to some other engineering plastics. Fillers are often added to enhance its mechanical properties.
- Difficult to Process: PTFE is challenging to process through traditional methods like injection molding and extrusion due to its high melting point and low melt viscosity.
- Relatively High Cost: Virgin PTFE can be more expensive than other plastics, especially when compared to those used in common applications.
Common Applications of PTFE
- Chemical Processing: PTFE is used for gaskets, seals, and linings in chemical processing equipment due to its exceptional chemical resistance.
- Oil and Gas Industry: PTFE is employed in oil and gas applications for seals, gaskets, and valve components due to its resistance to corrosive fluids.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: PTFE is used in medical devices like catheters, surgical implants, and lab equipment due to its biocompatibility and chemical resistance.
- Aerospace: PTFE is used in aerospace applications for seals, gaskets, and bearings due to its low friction, chemical resistance, and high temperature capability.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: PTFE is used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment due to its high-purity and non-contaminating properties.
- Electrical and Electronics: PTFE is employed in electrical insulation materials, cable jackets, and connectors due to its electrical insulating properties.
- Automotive: PTFE is used in automotive applications for seals, gaskets, bearings, and bushings due to its low friction and wear resistance.
- Food and Beverage Industry: PTFE is used in food processing equipment, conveyor belts, and non-stick coatings for cookware due to its non-toxicity and non-stick properties.
Please consult a Canyon Components Engineer about your specific application and we will use our decades of experience to formulate a solution that fits your need.
PTFE Plastic (Polytetrafluoroethylene, Teflon) Materials Available
This table shows many of our standard materials and links out to our O-ring store. Get in touch with us if you need a custom gasket, custom molded part, or non-standard geometry!
Filter by
Temperature Search (°C)
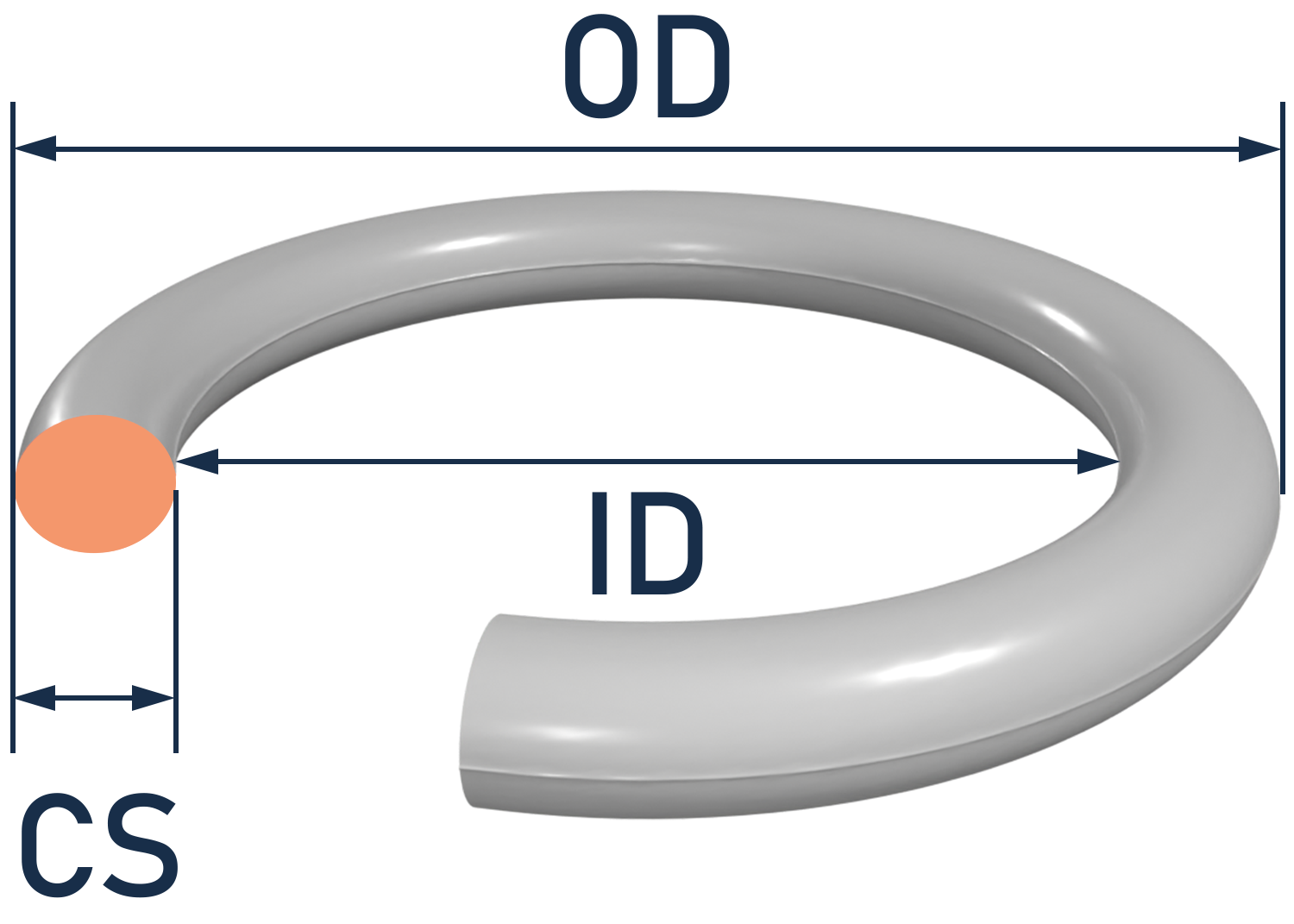
Types of PTFE
PTFE can come in different variations, depending on its composition and intended use. Some common types of PTFE include the following.
Canyon Components strives to meet all customer service requests. Feel free to contact Canyon Components engineering and let our knowledgeable staff help you design the perfect part for your needs.
Virgin PTFE
This pure form of PTFE is prized for its exceptional chemical resistance and non-stick properties. It's widely used in applications ranging from cookware coatings to chemical processing equipment. Virgin PTFE also exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for electronic components.
Filled PTFE
By incorporating fillers like glass fibers, carbon, or graphite, filled PTFE offers enhanced mechanical properties, such as increased wear resistance and thermal conductivity. It's suitable for high-load bearing applications and environments with high wear and tear, such as industrial seals and bearings.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
ePTFE is a highly porous, flexible, and lightweight form of PTFE. It's used in filtration, gaskets, and as a breathable membrane in textiles due to its ability to resist water while allowing air to pass through. Its high tensile strength also makes it useful in medical applications.
Modified PTFE
This variant has altered molecular structure to improve properties like deformation resistance under load. It's used in applications requiring enhanced creep resistance and reduced permeability, such as in complex gaskets and seals in the chemical and food processing industries.
PTFE Coatings
PTFE coatings are applied to various substrates to provide a non-stick, corrosion-resistant surface. Commonly used in cookware, bakeware, and industrial equipment, these coatings combine the benefits of PTFE with the convenience of an easy-to-apply surface.
PTFE Films and Sheets
These forms of PTFE are used for lining, insulation, and as a barrier material. They offer the full range of PTFE's chemical and temperature resistance properties in a flexible format. Applications include lining of pipes and tanks, electrical insulation, and as a slide bearing material in construction.
Please consult a Canyon Components Engineer about your specific application and we will use our decades of experience to formulate a solution that fits your need.
Manufacturing Options for PTFE
PTFE parts can be manufactured using several methods, each suitable for different applications and part complexities.
Each of these methods has its own advantages, limitations, and cost implications. The choice of manufacturing technique usually depends on factors like the complexity of the design, required precision, material properties, and production volume.
Canyon Components strives to meet all customer service requests. Feel free to contact Canyon Components engineering and let our knowledgeable staff help you design the perfect part for your needs.
PFAS in PTFE
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of man-made chemicals that include PFOA, PFOS, GenX, and many other chemicals. PFAS have been manufactured and used in various industries around the world since the 1940s. Due to their widespread use and persistence in the environment, PFAS are present in many materials and products, including some components we supply.
PTFE (CAS 9002-84-0; (C₂F₄)ₙ) is a fluoropolymer prized for its chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability, commonly used in nonstick coatings, seals, gaskets, and bearings.
The U.S. EPA, for purposes of TSCA § 8(a)(7) (40 CFR 705), considers any substance or mixture to be a PFAS if it contains at least one of these three molecular fragments:
(1) R-(CF2)-CF(R′)R″, where both the CF2 and CF moieties are saturated carbons;
(2) R–CF2 OCF2 -R′, where R and R′ can either be F, O, or saturated carbons; and
(3) CF3 C(CF3)R′R″, where R′ and R″ can either be F or saturated carbons.
This list isn’t exhaustive—additional chemicals meeting these criteria can be found via the EPA’s Central Data Exchange (CDX).
The European Union (EU) ECHA defines PFAS as:
any substance that contains at least one fully fluorinated methyl (–CF3) or methylene (–CF2–) carbon atom (without any H/Cl/Br/I attached to it).
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) defines PFAS as:
PFASs are defined as fluorinated substances that contain at least one fully fluorinated methyl or methylene carbon atom (without any H/Cl/Br/I atom attached to it), i.e. with a few noted exceptions, any chemical with at least a perfluorinated methyl group (–CF3) or a perfluorinated methylene group (–CF2–) is a PFAS.
Under the structural criteria established by the EPA, ECHA, and OECD, PTFE qualifies as a PFAS.
We are aware of the concerns regarding the environmental and health impacts of PFAS. As a responsible supplier, we are committed to transparency regarding the presence of PFAS in our products. We understand that certain applications and regulations may require components free from PFAS.
Please inform us if your application requires PFAS-free parts. We are dedicated to working with our customers to provide solutions that meet their specific needs, including sourcing and supplying PFAS-free components. Our team is available to discuss your requirements and ensure that the parts we supply meet your specifications.
Canyon Components LLC standard industrial parts are not intended for use in applications where exposure could cause harm. For applications that require testing & certification to be PFAS-free, Canyon Components LLC provides components that undergo necessary testing and certification requirements.
Canyon Components strives to meet all customer service requests. Feel free to contact Canyon Components engineering and let our knowledgeable staff help you design the perfect part for your needs.
Back to Plastics Hub

Get A Quote Now!

Groove Design References
Learn More
Coatings, Packaging, & Other Services
Learn More
Custom Parts & Custom O-rings
Learn More
